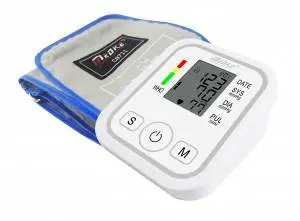
Many hypertensive patients have some questions about the accuracy of electronic sphygmomanometers, and are not sure whether their measurements are accurate when measuring blood pressure. At this time, people can use the blood pressure standard to quickly calibrate the accuracy of the electronic sphygmomanometer, find their own measurement deviations, and then measure the blood pressure. So, how to calibrate the electronic sphygmomanometer?
First of all, electronic sphygmomanometers use modern technology to measure blood pressure. Most patients with high blood pressure have spares in their homes. Electronic sphygmomanometers are divided into arm type and wrist type; its technology has experienced the development of the most primitive first generation, second generation (semi-automatic sphygmomanometer), and third generation (intelligent sphygmomanometer). The electronic sphygmomanometer has become the main tool for family self-measurement of blood pressure. Electronic sphygmomanometers are also increasingly used in hospitals and other medical institutions.
The sphygmomanometer used in the hospital is tested and calibrated once a year by the Quality Supervision Bureau. It is recommended to use an upper-arm electronic sphygmomanometer for household sphygmomanometers, because the wrist-type is located at the end of the artery and is far from the heart, which reduces the accuracy of measurement. In addition, household blood pressure It is also recommended to calibrate once a year.
The operation steps of a medical mercury sphygmomanometer to determine whether an electronic sphygmomanometer is accurate are as follows: first measure the blood pressure with a mercury sphygmomanometer. After resting for 3 minutes, measure the second time with an electronic sphygmomanometer. Then rest for another 3 minutes, and measure the third time with a mercury sphygmomanometer. Take the average of the first and third measurements. Compared with the second measurement with an electronic sphygmomanometer, the difference should generally be less than 5 mmHg.
In addition, wrist-type electronic sphygmomanometers are not suitable for elderly people because their blood pressure is already high and blood viscosity is high. The results measured by this type of sphygmomanometer have been lower than the blood pressure pumped by the heart itself. Many, this measurement result has no reference value.
Post time: Dec-31-2021